VISITING HOURS:
Week Days - 9 am to 8 pmSundays - Only Emergency Cases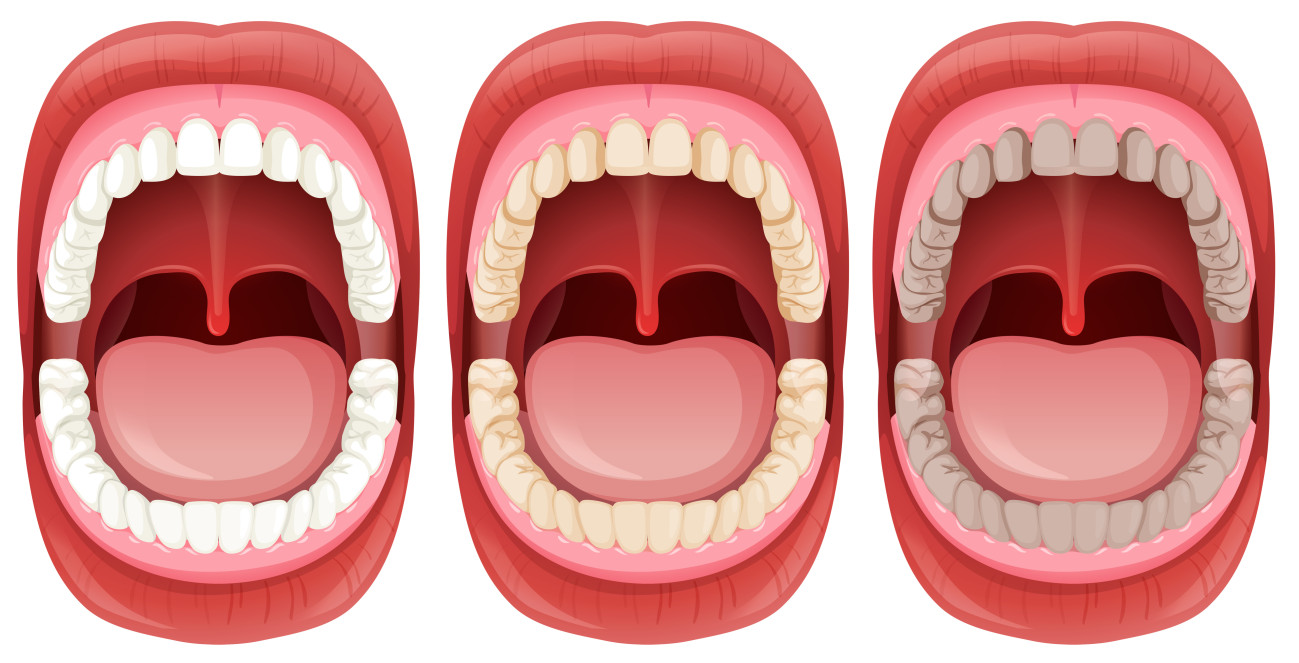
Tooth Erosion: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
What is Dental Erosion or Enamel Erosion?
Dental erosion, also known as enamel erosion, is a common problem that affects both adults and children. If not taken care of at the right time, it can lead to further complications. Tooth enamel is the hard exterior of the teeth. The purpose of tooth enamel is to protect the dentine layer of the teeth. Tooth enamel is the hardest mineral in the body, but once it is damaged, it is permanent and eventually will wear away completely.
Numerous studies have identified food and drink consumption as the primary causes of tooth erosion. The acidic nature of the food consumed can have major effects on the enamel of the tooth. There are many other factors that cause tooth erosion, and we will see them in the next heading.
Causes of Dental Erosion
The six main causes of dental erosion are dietary, regurgitation, environmental, flow of saliva, aging, and idiopathic. Let us try and get to know each of these causes.
Dietary
Food and beverages are the main contributors to dietary and gastric acid formation in the mouth. These acids attack the calcium mineral on the enamel and cause it to erode. Carbonated beverages and drinks with high citrus content have the highest acid content and can be responsible for tooth erosion when consumed frequently.
Regular consumption of citric acid in soft drinks, acidic sugar-free drinks, sugary drinks, and acidic fruits can play a major role in dental erosion.
Regurgitation
When the digestion process takes place within the system, an acid is formed to enhance the breakdown of the food particles. The acids that are then formed are easy to break down, even in teeth and bones. When the contents of the stomach come back to the mouth as part of gastric reflux and this continues for a long period of time, then it might be a cause for dental erosion.
The acids from gastric reflux or regurgitation first affect the back of the teeth. The erosion is seen as a faded yellowish tint on the back of the teeth. This tint means that the dentine of the surface is now exposed. When this happens, the mouth becomes overly sensitive to the intake of sweet, sour, hot, and cold food. When the erosion goes deeper, it can start affecting the nerves and muscles of the mouth as well.
Flow of Saliva
Saliva plays a major role in the digestive process of the human body. It helps break down the food we are consuming. It also helps neutralize the buildup of plaque in the mouth, which is an aftermath of the acidic byproduct of oral bacteria. When there is less flow of saliva in the mouth, it can cause an increase in the acidic level of the mouth and can result in dental or enamel erosion.
Environmental Factors
People who work in dangerous environments and are constantly exposed to hazardous chemicals are more prone to dental erosion. Working in plants and mines, where fumes can cause erosion, is a common cause. If you are someone who spends a lot of time in chlorinated water, like in swimming pools, then you might also come into contact with the issue of dental erosion.
Aging
Aging can be one of the common causes of dental erosion. As the person gets older, it can be subject to normal wear and tear of the enamel of the teeth. It can be avoided by maintaining a good oral hygiene routine.
Idiopathic
Idiopathic tooth erosion happens without any specific cause.
Read to know : Best 9 Practices For Healthy Teeth and Gums
Symptoms of Dental Erosion
Long before the physical damage manifests in the teeth, a person can experience enamel erosion in the mouth as pain or high sensitivity. Tooth sensitivity prevents chewing and, in particular, hot or cold food consumption. The main symptoms of dental erosion will be:
Toothache and intense sensitivity.
Discoloration of the teeth; starts turning extremely yellowish.
Transparency around the front teeth’s edges
Teeth with an unusually rounded appearance
Chalky pits or cracks on the teeth.
The rough appearance of the teeth.
Make sure to book an appointment when you first start having toothache and sensitivity around your tooth.
Also Read: Tooth discoloration: Reasons, Prevention and Treatment
Treatment for Enamel or Tooth Erosion
The type of symptom determines the treatment for enamel erosion. A patient usually goes to the dentist when they face pain in the teeth, chipped teeth, high sensitivity, or any of the other symptoms of enamel erosion. The dentist examines your condition, suspects the extent to which the tooth erosion has happened, and suggests medical treatment accordingly. The usual treatments considered for enamel erosion are:
Dentists perform fillings for areas where there is minor erosion and the erosion is localized in one small area.
Dentists use crowns when filling cannot compensate for the erosion that has covered a major area.
Dental Bonding helps support multiple teeth.
Veneers for permanent protection against erosion.
Dentists recommend root canals when erosion has deeply affected the roots. If it is not possible to repair the tooth using root canals, then the only option left is to extract the tooth.
Read to know: Are Dental Veneers Right for You?
Preventive Measures Against Tooth Erosion
There are many ways in which one can easily prevent tooth erosion. It is to make sure that you perform a good oral hygiene routine in your day-to-day life. Here are those measures:
Reducing the intake of sugary or acidic foods, like sweets and carbonated drinks.
Drinking water along with the consumption of citrusy and acidic foods.
If you have a tendency for enamel erosion, the dentists might recommend you to have specific chewing gum that will help stimulate saliva and wash off the acidic buildup.
Make sure to accompany acidic or citrusy foods with other meal components.
Rinsing your mouth well after having acidic foods. Do not brush your teeth right after as the enamel of your teeth is soft and brushing can cause more damage. Similar is the case when you vomit or have acid reflux.
Accompany your dental hygiene with toothpaste and toothbrush as recommended by the dentist.
Poor oral hygiene causes tooth erosion, and you can prevent it by implementing good standards for keeping your mouth clean.
OUR
TREATMENTS
TREATMENTS